
Top Peptide Api Manufacturing Techniques and Innovations Explained?
The world of peptide API manufacturing is rapidly evolving. Innovations continually reshape how these vital compounds are produced. These advancements enhance efficiency and ensure high-quality output, but not without challenges.
Peptide API manufacturing relies on precise techniques. Each procedure must be finely tuned to safeguard purity and efficacy. The complexity of peptide synthesis presents hurdles, often requiring experimentation and adjustment. Some manufacturers experiment with various solvents and reagents but may face scalability issues.
The industry reflects innovation and struggle. New protocols emerge, striving for better yields and reduced costs. However, issues such as lengthy production times and stringent regulations remain. As the demand for peptides rises, manufacturers must balance innovation with practical limitations. The journey of peptide API manufacturing is both promising and filled with potential pitfalls.
Overview of Peptide Production and Its Importance in Biotechnology
Peptide production plays a crucial role in biotechnology. It serves as a basis for drugs and therapies. According to a 2021 industry report, the peptide therapeutics market is expected to reach $46.8 billion by 2025. This growth reflects the rising demand for targeted therapies in medicine. Peptides are known for their precision in treating diseases compared to traditional medications.
The manufacturing techniques for peptides have seen significant innovations. Solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) is a widely used method. SPPS allows for precise control during synthesis. However, this method can be time-consuming and expensive. Improvements in automation could reduce costs and increase efficiency. Additionally, the emergence of continuous-flow processes shows promise for large-scale production.
**Tip:** Consider the importance of optimizing production methods to enhance yield and reduce costs.
While innovations are promising, challenges remain. Quality control is essential in peptide production. Impurities can affect drug efficacy. According to a study, more than 30% of produced peptides do not meet purity standards. Continuous monitoring is vital for developing reliable therapies.
**Tip:** Implement stringent quality control protocols throughout the production process.
Top Peptide Production Techniques and Innovations
Key Techniques in Peptide Synthesis: A Comprehensive Overview
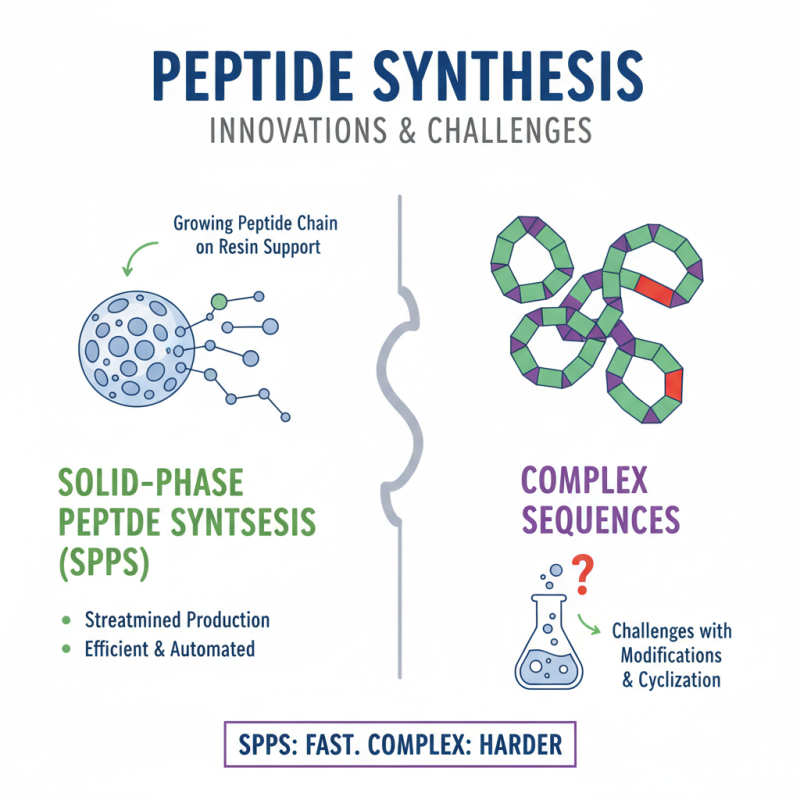
Peptide synthesis has gained significant attention in recent years. The techniques involved are both fascinating and complex. Solid-phase synthesis is a widely adopted method. It allows for a more streamlined production process. This method involves attaching a growing peptide chain to a solid resin. The process is efficient but can be challenging when adding complicated sequences.
Another technique is liquid-phase synthesis. While it can be less efficient than solid-phase synthesis, it has its own advantages. It allows for easier purification of the final product. However, achieving high yields can be tricky. The chemist must carefully control reaction conditions. This technique often demands a more hands-on approach, leading to potential inconsistencies.
The emergence of automation in peptide synthesis offers promise. Automation can reduce human error and increase efficiency. Yet, it is not foolproof. Automated systems require regular maintenance and calibration. There is strong reliance on technology, which can sometimes lead to unexpected challenges. As innovations unfold, stakeholders must remain aware of the evolving landscape of peptide manufacturing. Adapting to new techniques is essential for consistent quality and yield.
Recent Innovations in Peptide Manufacturing Technology
Recent innovations in peptide manufacturing technology are transforming the landscape of biopharmaceutical production. Automation plays a key role. Streamlined processes are increasing efficiency and reducing human error. Advanced robotics can carry out repetitive tasks consistently. However, these machines require significant upfront investments. It's crucial to balance the cost against potential long-term savings.
Another area of focus is the development of new synthesis methods. Solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) has become widely used. Scientists are also experimenting with microwave-assisted techniques. These methods can reduce synthesis time dramatically. Yet, they may not be suitable for all peptide types. Ongoing research is necessary to optimize these approaches for diverse applications.
Quality control remains a critical aspect. Innovations in analytical techniques are helping manufacturers meet regulatory standards. Mass spectrometry and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) allow for precise characterization. Still, these techniques can be complex and require skilled personnel. There is an ongoing need for user-friendly solutions that improve accessibility. Balancing innovation with practical application is key to advancing peptide manufacturing technology.
Top Peptide API Manufacturing Techniques and Innovations Explained
| Technique | Description | Recent Innovations | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solid-Phase Peptide Synthesis (SPPS) | A method for assembling peptides on a solid support | Automation and continuous flow synthesis | Increased efficiency and scalability |
| Liquid-Phase Peptide Synthesis (LPPS) | Synthesis conducted in a liquid medium | Enhanced coupling reagents | Improved yield and purity |
| Microwave-Assisted Peptide Synthesis | Utilizing microwave energy to accelerate reactions | Smart microwave reactors with better temperature control | Faster synthesis times and enhanced quality |
| Deep Learning in Peptide Design | Using AI algorithms to predict peptide stability and activity | Integration of deep learning models | Enhanced design efficiency and target specificity |
Challenges in Peptide API Production and Quality Control
The production of peptide APIs presents several challenges. One significant issue is maintaining consistency in quality. Peptides are sensitive to environmental changes. Even small variations in temperature or pH can alter their structure and efficacy. Manufacturers must implement stringent controls to ensure each batch meets required specifications.
Quality control processes can be resource-intensive. Techniques like HPLC and mass spectrometry are essential. However, these methods can be time-consuming and costly. There are cases where batches fail to meet quality standards. This can lead to production setbacks and financial loss. Companies need to balance analytical depth with efficiency.
Moreover, scaling up production introduces additional complexities. Techniques suitable for small batch sizes may not work on a larger scale. This disparity can compromise the quality of the final product. It raises questions about the optimization of processes. Continuous improvement and innovation in manufacturing techniques are critical. Emphasizing training for personnel can also enhance quality control.
Future Trends in Peptide API Development and Manufacturing Techniques
The future of peptide API development is rapidly evolving. Innovations in manufacturing techniques are crucial for improving efficiency and scalability. According to a recent industry report, the global peptide therapeutics market is estimated to reach $48.6 billion by 2026, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.6%. This rapid growth indicates a rising demand for advanced manufacturing methods.
One notable trend is the move towards greener synthesis methods. Traditional peptide synthesis can generate significant waste. Newer technologies focus on minimizing by-products and utilizing environmentally friendly solvents. For example, researchers have shown that using alternative coupling agents can increase yields while reducing harmful emissions. This shift is essential for sustainable practices in peptide API production.
Moreover, automation is transforming the landscape of peptide manufacturing. Automated platforms enable higher throughput and consistency. However, they require significant upfront investment and training. Many companies struggle with this transition, risking potential delays. The integration of AI in process optimization offers a glimpse into the future. Still, the effectiveness of these systems is yet to be fully realized. As the industry adapts, ongoing challenges in cost and regulatory compliance will need continuous reflection.
Related Posts
-

Maximizing ROI: The After-Sales Service Edge in Best Peptide API Manufacturing
-

Ultimate Guide to Sourcing the Best Peptide Api Manufacturing for Your Business Needs
-

Top 10 Tips for Efficient Peptide API Manufacturing Process
-

10 Best Practices for Peptide API Manufacturing to Maximize Efficiency
-

How to Effectively Scale Peptide API Manufacturing for Optimal Yield and Purity
-

Exploring Peptide Api Manufacturing Opportunities at 2025 China 138th Canton Fair with Market Growth Insights
