
What Are the Best Materials for Drug Capsules?
Selecting the right Drug Capsule Material is crucial for effective medication delivery. Different materials possess unique properties that impact drug stability and release. For instance, gelatin is commonly used for its ease of production and bioavailability.
Conversely, vegetarian alternatives like HPMC (hydroxypropyl methylcellulose) are gaining popularity. They suit those seeking plant-based options. Each material affects how the body absorbs the drug. Some combinations may cause inconsistencies in dissolution rates. Striking the right balance can be challenging.
Additionally, factors like shelf life and patient preference must be considered. The market is evolving, yet many questions remain. Are we prioritizing efficacy over patient comfort? This continuous need for improvement in Drug Capsule Materials highlights the complexities of pharmaceutical development.

Overview of Drug Capsule Materials
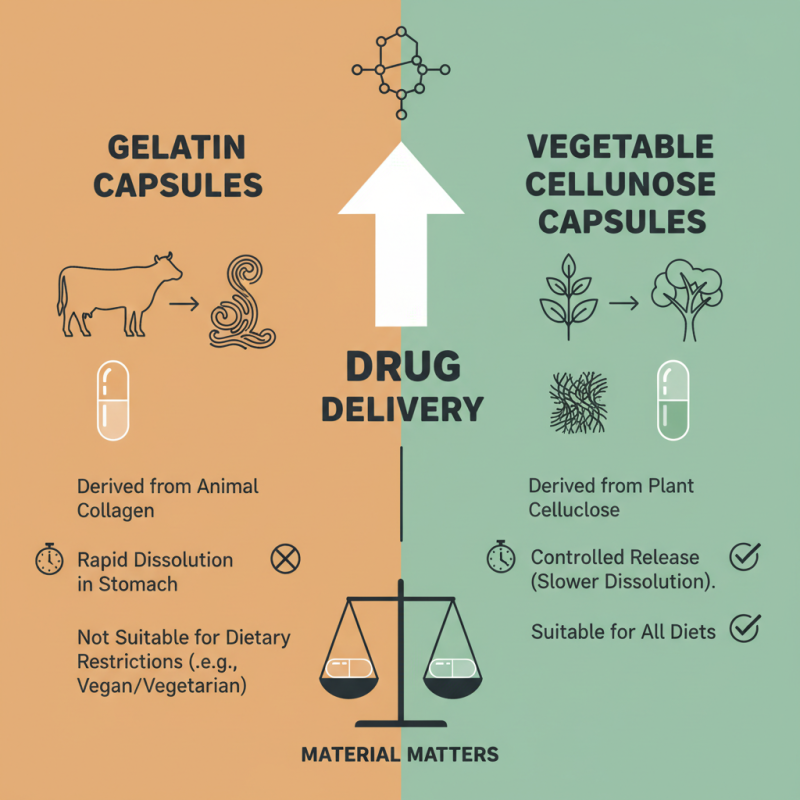
Drug capsules are a popular method for delivering medications effectively. The materials used for these capsules can significantly impact their performance. Gelatin and vegetable cellulose are the two most common materials. Gelatin is derived from animal collagen. It is known for its quick dissolution in the stomach. However, some people may have dietary restrictions that limit its use.
Vegetable cellulose, on the other hand, is a great alternative. It is suitable for vegetarians and those with allergies. This material is derived from plant sources. It tends to dissolve slower than gelatin. This slow dissolution can be beneficial for controlled-release applications. Yet, the formulation may sometimes contain additives that could affect its efficacy.
Choosing the right material for drug capsules is crucial. It is essential to balance the speed of dissolution with the needs of the patient. The choice may involve trade-offs. For instance, the cost of materials can vary widely. This could impact the pricing of the final product. Understanding these nuances is key to optimizing capsule design. Each patient's needs should drive these decisions.
Types of Materials Used in Drug Capsules
Capsules have become a popular choice for drug delivery due to their versatility and ease of use. The materials used for these capsules significantly impact their performance. Gelatin is one of the most common materials. It is derived from animal collagen and is known for its ability to dissolve quickly in the stomach.
A report by Research and Markets suggests that gelatin capsules hold around 70% of the market share due to their favorable properties.
Another popular alternative is HPMC, or Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose. Unlike gelatin, HPMC is plant-based and appeals to vegetarian and vegan consumers. Its use has been steadily increasing, with a growth rate forecast of 6% annually. This material offers better stability under various conditions, making it suitable for a range of formulations.
Tips: When selecting capsule materials, consider stability. The choice can affect drug release. Also, think about patient dietary restrictions.
Some materials like pullulan are gaining attention. Pullulan is a polysaccharide that offers excellent oxygen barrier properties. This ensures the stability of sensitive ingredients. However, it is more expensive and might not be as widely available as gelatin or HPMC.
Tips: Look for cost-effective alternatives. Sometimes, the cheapest option doesn't mean the best quality. Always conduct thorough research.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Various Capsule Materials
The choice of materials for drug capsules can significantly impact their effectiveness. Gelatin capsules are popular due to their versatility. They dissolve quickly in the stomach, providing rapid drug release. According to a report by the International Journal of Pharmaceutics, gelatin capsules can achieve a dissolution rate of 90% within 15 minutes. However, they may not be suitable for all users, particularly those with dietary restrictions.
Vegetable-based capsules, such as those made from hypromellose, offer an alternative. These capsules are plant-derived and suitable for vegetarians. They can also withstand higher humidity levels, making them useful for various environments. On the downside, hypromellose capsules may have slower dissolution rates than gelatin, averaging around 45 minutes in some studies.
Another option is enteric-coated capsules. They protect sensitive ingredients from stomach acid and ensure release in the intestines. This feature is beneficial for probiotics or certain nutrients. Nevertheless, enteric coatings can complicate manufacturing and may not always be reliable in achieving the intended release profiles, according to research published in the European Journal of Pharma and Biopharma. The choice of capsule material calls for careful consideration, balancing benefits against potential drawbacks.
Factors Influencing Material Selection for Capsules
When selecting materials for drug capsules, several factors come into play. The intended release profile is crucial. Some capsules require a quick release, while others need to be slow-digesting. This influences the choice between gelatin, HPMC, or even starch-based materials. Each material has unique properties that affect how the drug interacts.
It's also essential to consider the drug's stability. Certain drugs may react with specific capsule materials. For instance, moisture-sensitive drugs might require more protective enclosures. Assessing the compatibility of the drug with the capsule is a vital step.
**Tips:** Look for capsules with good barrier properties. This can help maintain drug integrity. Also, always test small batches before full production. Small changes can lead to significant results. Finally, consider the environmental impact of your capsule materials. Sustainability plays a growing role in pharmaceutical development.
What Are the Best Materials for Drug Capsules?
This chart displays the popularity scores of various materials used for drug capsules. Gelatin remains the most popular choice due to its favorable properties for capsule formulation, while HPMC and Pullulan are recognized as viable alternatives, particularly for vegetarian options.
Future Trends in Capsule Material Development
The future of capsule materials is evolving rapidly. Researchers are exploring alternatives to traditional gelatin. Plant-based polymers are gaining traction. They are suitable for vegetarians and provide an eco-friendly option. However, formulation challenges remain.
The demand for personalized medicine continues to grow. This trend has sparked interest in tailored capsule materials. New technologies enable microencapsulation of complex drugs. This method can enhance bioavailability. Yet, ensuring stability can be tricky.
Nanotechnology is another area of focus. It opens doors to innovative capsule designs. These capsules might offer targeted drug delivery. However, the potential toxicity of nanoparticles raises concerns. Balancing effectiveness and safety is essential in this field. The path ahead is filled with both excitement and uncertainty.
What Are the Best Materials for Drug Capsules? - Future Trends in Capsule Material Development
| Material Type | Advantages | Disadvantages | Current Trends |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gelatin | Easy to swallow, excellent bioavailability, well-established | Animal-derived, risk of allergies, not suitable for vegetarians | Development of vegetarian alternatives, improvements in sourcing |
| HPMC (Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose) | Vegetarian-friendly, stable under various conditions, customizable | Longer dissolution time compared to gelatin, potential for higher costs | Increasing focus on plant-based products, enhanced formulation techniques |
| Pullulan | Natural, biodegradable, high oxygen barrier properties | Limited commercial availability, generally higher production costs | Growing interest due to environmental impact, research on production methods |
| Starch-based capsules | Biocompatible, cost-effective, suitable for various fillings | Can be less robust, moisture sensitivity | Innovative modifications for enhancing performance, eco-friendly initiatives |
Related Posts
-

Unlocking Opportunities in Medicine Capsule Material at the 137th Canton Fair for Global Buyers
-

How to Choose the Best Drug Capsule Material for Your Pharmaceutical Needs
-

How to Choose the Best Medicine Capsule Material for Your Pharmaceutical Needs
-

How to Choose the Right Medicine Capsule Material for Effective Drug Delivery
-

Exploring Pharmaceutical Supply Trends at the 138th Canton Fair in China 2025
-

2026 Best Pharmaceutical Testing Methods for Quality Assurance?
